Business inventory policies are the backbone of efficient inventory management, shaping how businesses procure, store, and distribute their products. Understanding these policies is crucial for optimizing inventory levels, ensuring customer satisfaction, and driving business success.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of business inventory policies, exploring their objectives, types, design principles, implementation strategies, evaluation methods, and industry-specific considerations. Embark on this journey to unlock the power of effective inventory management.
Inventory Management Fundamentals: Business Inventory Policies
Inventory management is the backbone of any business that involves the storage and management of physical goods. It encompasses the processes of acquiring, storing, and distributing inventory to meet customer demand while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency.
Inventory policies are a set of guidelines that dictate how a business manages its inventory. They establish the rules and procedures for determining inventory levels, replenishment strategies, and stock management. Implementing effective inventory policies is crucial for businesses to optimize their operations, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction.
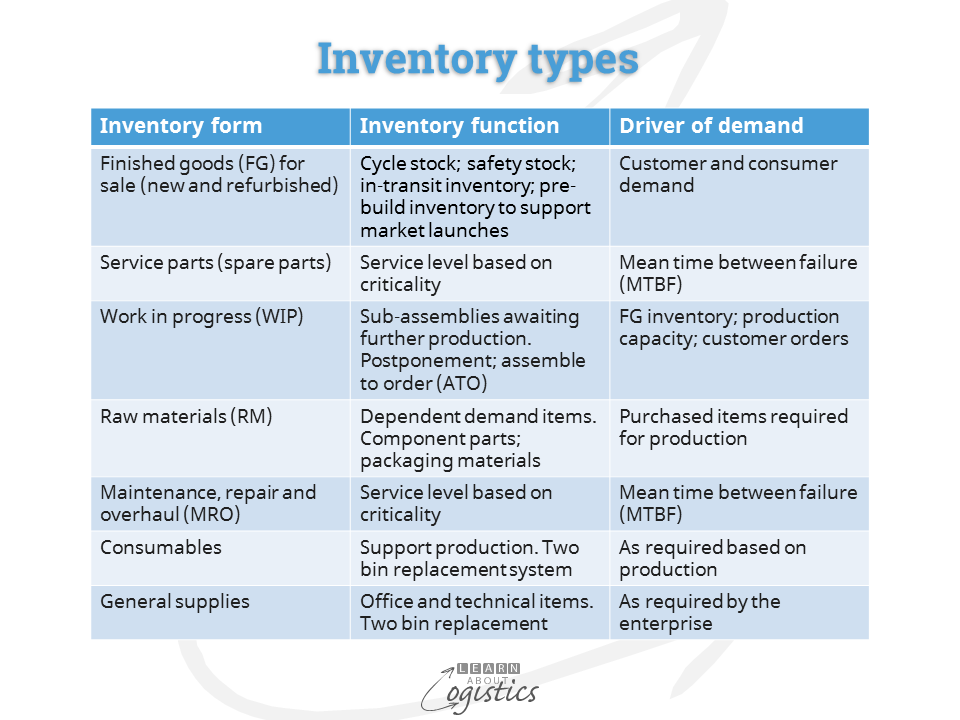
Types of Inventory Policies
There are several different types of inventory policies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types include:
- Fixed-order-quantity policy: This policy involves ordering a fixed quantity of inventory whenever the inventory level falls below a predetermined reorder point.
- Fixed-order-interval policy: This policy involves ordering inventory at regular intervals, regardless of the current inventory level.
- Periodic-review policy: This policy involves reviewing inventory levels at regular intervals and ordering enough inventory to bring the inventory level up to a predetermined target level.
Inventory Policy Objectives
Inventory policies serve as guiding principles for managing inventory levels, ensuring optimal stock levels and efficient inventory management. These policies establish clear guidelines for maintaining appropriate inventory levels, minimizing costs, and meeting customer demand effectively.
Role in Optimizing Inventory Levels
Inventory policies play a crucial role in optimizing inventory levels by balancing the trade-off between holding costs and stockout costs. They determine the target inventory levels, reorder points, and safety stock levels, ensuring that inventory is neither excessive nor insufficient.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction, Business inventory policies
Inventory policies directly impact customer satisfaction by influencing the availability of products and the timeliness of order fulfillment. Effective inventory policies minimize stockouts, reduce lead times, and ensure that customers receive their orders promptly, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Inventory Policy Evaluation and Improvement
Evaluating and improving inventory policies are crucial for optimizing inventory management and achieving business objectives. Effective inventory policies ensure optimal stock levels, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. This section explores methods for evaluating inventory policies, key metrics, and the process of making adjustments and improvements.
Metrics for Inventory Policy Evaluation
Key metrics and performance indicators provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of inventory policies. Some common metrics include:
- Inventory turnover ratio: Measures how efficiently inventory is converted into sales.
- Days inventory outstanding (DIO): Indicates the average number of days inventory is held before being sold.
- Inventory carrying costs: The cost of holding inventory, including storage, insurance, and handling.
- Stockout rate: The percentage of customer orders that cannot be fulfilled due to insufficient inventory.
- Customer service level: The percentage of customer orders that are fulfilled on time and in full.
Process of Making Adjustments and Improvements
Evaluating inventory policies involves analyzing metrics, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments. The process typically includes the following steps:
- Gather data and analyze metrics: Collect data on inventory levels, costs, and customer service levels.
- Identify areas for improvement: Analyze metrics to identify areas where inventory policies can be improved, such as reducing stockouts or lowering carrying costs.
- Develop and implement improvements: Develop and implement new inventory policies or make adjustments to existing ones to address the identified areas for improvement.
- Monitor and evaluate: Monitor the impact of the implemented changes and make further adjustments as needed to ensure continuous improvement.
By regularly evaluating and improving inventory policies, businesses can optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction, ultimately contributing to overall business success.
Special Considerations
Inventory policies are not one-size-fits-all. They must be tailored to the specific industry or business type. For example, a manufacturing company will have different inventory needs than a retail store. Similarly, a company that operates in a volatile supply chain environment will need to have a more flexible inventory policy than a company that operates in a stable environment.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions on Inventory Policies
Supply chain disruptions can have a significant impact on inventory policies. When a supply chain disruption occurs, it can lead to shortages of raw materials or finished goods. This can force companies to increase their inventory levels in order to avoid stockouts.
However, holding excess inventory can be expensive and can tie up cash flow. Companies need to carefully weigh the costs and benefits of increasing their inventory levels in response to supply chain disruptions.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Inventory Policy Management
There are a number of emerging trends and innovations in inventory policy management. One trend is the use of data analytics to improve inventory forecasting. By using data analytics, companies can better predict demand and optimize their inventory levels. Another trend is the use of automation to streamline inventory management processes.
Automation can help companies reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Last Recap
In conclusion, business inventory policies are indispensable tools for businesses seeking to optimize their inventory operations. By aligning these policies with their objectives, leveraging data-driven insights, and embracing technological advancements, organizations can effectively manage their inventory, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in the dynamic business landscape.
