Business central negative inventory, a perplexing situation where inventory records indicate a deficit, is a common challenge faced by businesses. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, prevention, and management of negative inventory in Business Central, providing valuable insights to help businesses maintain accurate inventory levels and optimize operations.
Negative inventory can arise from various factors, including human error, system glitches, or discrepancies in inventory counting. Understanding the root causes is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures.
Business Central Negative Inventory Overview

In Business Central, negative inventory occurs when the system records a negative quantity on hand for a particular item. This can happen due to various reasons, including errors in inventory transactions, returns, or adjustments.
Negative inventory can lead to several problems, such as incorrect financial reporting, inaccurate inventory valuation, and difficulty in fulfilling customer orders.
Causes of Negative Inventory
Some of the common causes of negative inventory in Business Central include:
- Incorrect inventory transactions: This can occur due to human error or system glitches, leading to incorrect quantities being recorded in the system.
- Returns: When customers return items, the inventory quantity should be increased. However, if the return process is not handled correctly, it can result in a negative inventory balance.
- Adjustments: Inventory adjustments are used to correct inventory quantities. If adjustments are not made accurately, they can lead to negative inventory.
Impact of Negative Inventory
Negative inventory can have several negative impacts on business operations, including:
- Incorrect financial reporting: Negative inventory can lead to inaccurate financial reporting, as the value of inventory is understated.
- Inaccurate inventory valuation: Negative inventory can make it difficult to accurately value inventory, which can impact decision-making.
- Difficulty in fulfilling customer orders: Negative inventory can make it difficult to fulfill customer orders, as the system may indicate that items are available when they are not.
Identifying and Preventing Negative Inventory
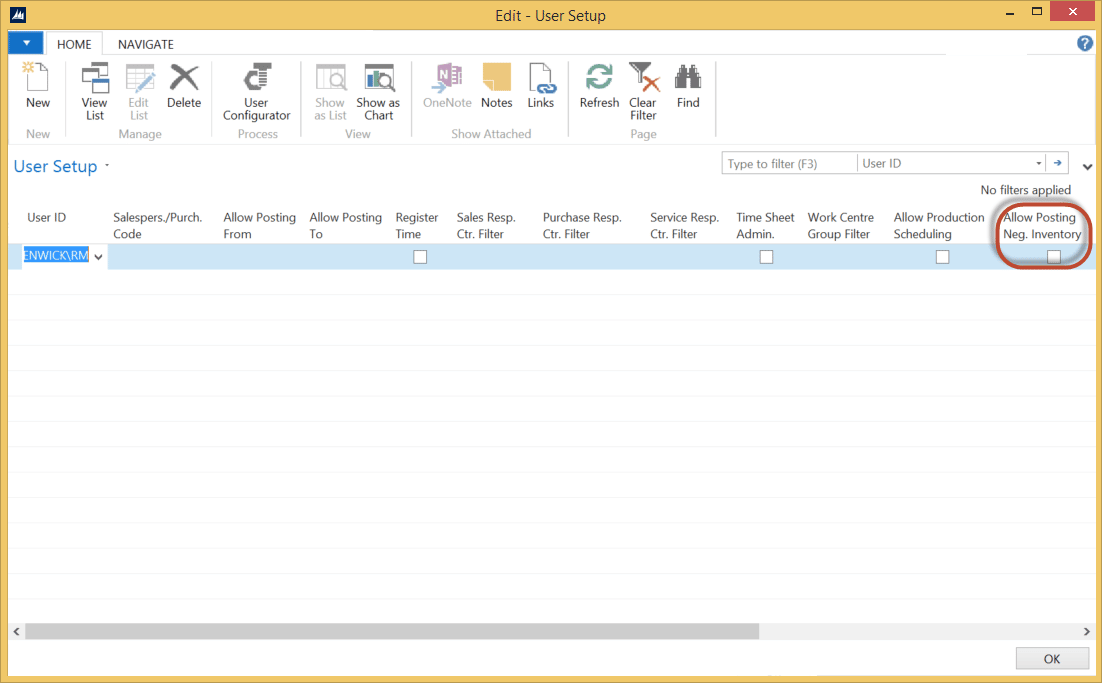
Negative inventory in Business Central can lead to inaccurate financial reporting, operational inefficiencies, and customer dissatisfaction. Identifying and preventing negative inventory is crucial for maintaining a healthy inventory management system.
Methods for Identifying Negative Inventory
To identify negative inventory in Business Central, follow these methods:
- Run the Inventory Status report:This report provides a snapshot of inventory levels, including negative balances.
- Check the Item Card:On the Item Card, navigate to the Inventory tab and review the Quantity on Hand field. Negative values indicate negative inventory.
- Use the Adjust Inventory feature:When adjusting inventory, Business Central will alert you if the adjustment would result in a negative inventory.
Strategies for Preventing Negative Inventory
To prevent negative inventory from occurring, consider these strategies:
- Maintain Accurate Inventory Records:Regularly reconcile inventory counts with physical stock to ensure accuracy.
- Use a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory costing method:This method assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, preventing the accumulation of obsolete inventory.
- Set Minimum and Maximum Stock Levels:Define minimum and maximum inventory levels to trigger alerts when inventory falls below or exceeds these thresholds.
- Implement a Warehouse Management System (WMS):A WMS can automate inventory tracking and prevent errors that lead to negative inventory.
Importance of Accurate Inventory Management Practices, Business central negative inventory
Accurate inventory management practices are essential for preventing negative inventory. These practices include:
- Regular Inventory Counts:Conduct physical inventory counts to verify the accuracy of inventory records.
- Cycle Counting:Perform periodic cycle counts to identify and correct inventory discrepancies.
- Inventory Reconciliation:Reconcile inventory records with purchase orders, sales orders, and other relevant documents.
By following these methods, strategies, and practices, businesses can effectively identify and prevent negative inventory, ensuring accurate financial reporting, efficient operations, and satisfied customers.
Managing Negative Inventory
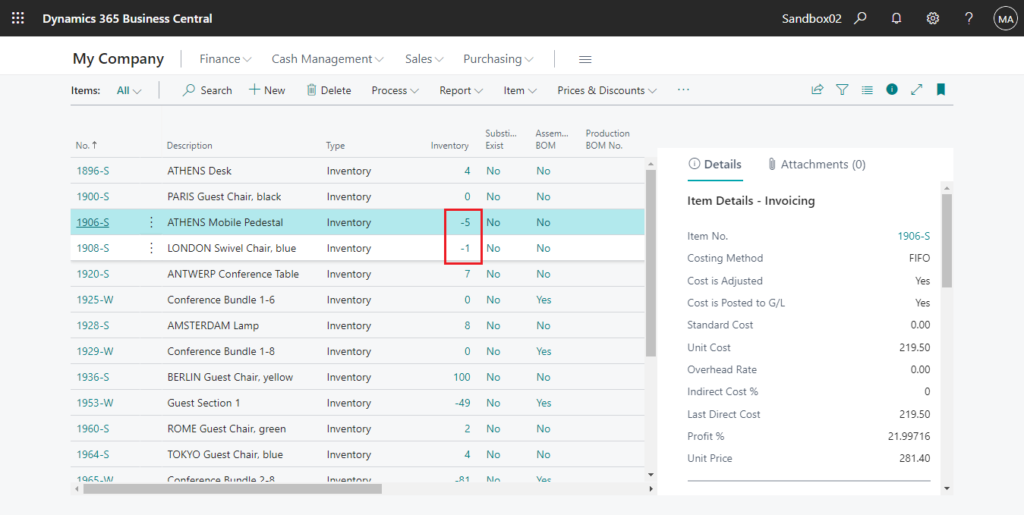
Negative inventory is a situation where the system shows a negative quantity for an item. This can occur due to various reasons such as incorrect transactions, errors in counting, or system glitches. Managing negative inventory is crucial to ensure accurate inventory records and prevent operational issues.
There are several methods to adjust negative inventory in Business Central. One common approach is to perform a manual adjustment. This involves creating an inventory adjustment journal and manually adjusting the quantity of the affected item to a positive value.
Another method is to perform an inventory recalculation. This process involves comparing the system’s inventory records with the physical inventory count. Any discrepancies between the two are automatically adjusted by the system.
Risks and Considerations
- Inaccurate Inventory Records:Negative inventory can lead to inaccurate inventory records, which can impact financial reporting, order fulfillment, and purchasing decisions.
- Operational Issues:Negative inventory can cause operational issues such as backorders, delayed shipments, and customer dissatisfaction.
- Loss of Revenue:In extreme cases, negative inventory can result in lost revenue if orders cannot be fulfilled due to insufficient stock.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to implement robust inventory management practices, such as regular inventory counts, accurate transaction processing, and periodic reconciliations.
Best Practices for Avoiding Negative Inventory: Business Central Negative Inventory
To minimize the risk of negative inventory, businesses should adopt proactive inventory management practices. Regular inventory audits and cycle counting are crucial for identifying and rectifying discrepancies.
Technology plays a significant role in preventing negative inventory. Inventory tracking systems provide real-time visibility into stock levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about replenishment and sales.
Inventory Audits and Cycle Counting
- Conduct regular inventory audits to verify the accuracy of inventory records.
- Implement cycle counting, a process of counting inventory on a rotating basis, to identify and correct discrepancies.
- Use technology, such as barcode scanners and RFID tags, to automate inventory counting and improve accuracy.
Technology-Enabled Inventory Management
- Utilize inventory tracking systems to monitor stock levels in real time.
- Set up automated replenishment processes to ensure that inventory levels are maintained at optimal levels.
- Integrate inventory management systems with other business systems, such as accounting and sales, to ensure data accuracy.
Summary
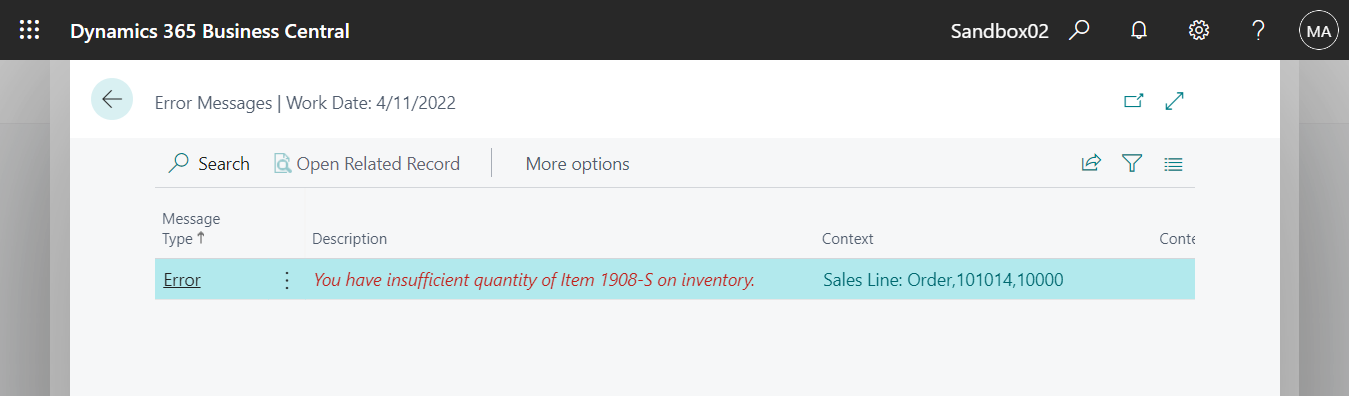
Managing negative inventory requires a systematic approach, involving identifying the extent of the issue, adjusting inventory records, and implementing measures to prevent its recurrence. Regular inventory audits, cycle counting, and leveraging technology for inventory tracking can significantly minimize the risk of negative inventory and ensure accurate inventory management.
