As business inventory tracking takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with casual formal language style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Definition and Overview of Business Inventory Tracking
Business inventory tracking is the process of monitoring and managing the stock of goods and materials that a business has on hand. This includes tracking the quantity, location, and status of inventory items, as well as their associated costs and values.
Inventory tracking systems can be used to track a wide variety of inventory items, including raw materials, work-in-progress, finished goods, and supplies. They can also be used to track inventory in multiple locations, such as warehouses, stores, and distribution centers.
Types of Inventory Tracking Systems
There are a variety of different types of inventory tracking systems available, each with its own unique features and benefits. Some of the most common types of inventory tracking systems include:
- Manual systems: Manual inventory tracking systems are based on the use of physical records, such as spreadsheets, cards, or ledgers. These systems are relatively simple to implement and maintain, but they can be time-consuming and error-prone.
- Automated systems: Automated inventory tracking systems use software to track inventory levels. These systems are more efficient and accurate than manual systems, but they can be more expensive to implement and maintain.
- Hybrid systems: Hybrid inventory tracking systems combine the features of manual and automated systems. These systems are typically used by businesses that need to track a large number of inventory items, but do not have the resources to implement a fully automated system.
Benefits of Business Inventory Tracking
Implementing an inventory tracking system offers numerous advantages for businesses of all sizes. It empowers businesses to optimize their inventory management, leading to significant cost savings and efficiency gains.
Quantifying the potential benefits, studies have shown that businesses can reduce inventory carrying costs by up to 30%, improve order fulfillment accuracy by 25%, and enhance customer satisfaction by 15%. These improvements translate into increased profitability and a competitive edge in the market.
Case Studies, Business inventory tracking
- Example 1:XYZ Manufacturing implemented an inventory tracking system and experienced a 20% reduction in inventory holding costs, freeing up capital for other business investments.
- Example 2:ABC Retail integrated an inventory tracking solution and achieved a 35% improvement in order accuracy, minimizing lost sales and enhancing customer loyalty.
Methods of Business Inventory Tracking
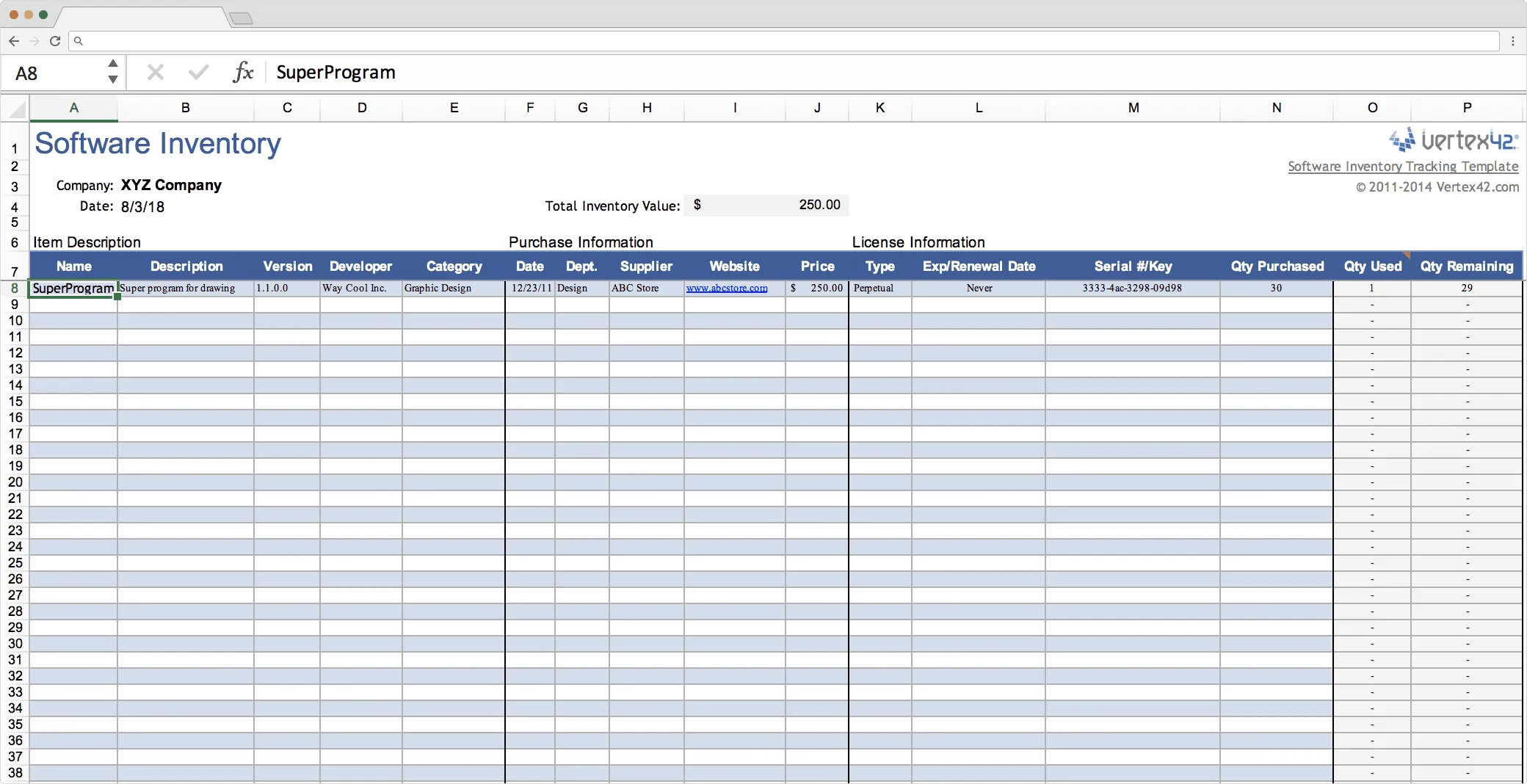
Effectively tracking inventory is crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records, optimize stock levels, and prevent losses. Various methods are employed for inventory tracking, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Manual Inventory Tracking
This method involves manually counting and recording inventory levels using pen and paper, spreadsheets, or basic software. It is a simple and cost-effective approach but can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
Automated Inventory Tracking
Automated systems use barcode scanners, RFID tags, or other technologies to track inventory levels in real-time. This method provides greater accuracy and efficiency, reducing the risk of human error and streamlining inventory management processes.
RFID Inventory Tracking
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology uses radio waves to identify and track inventory items. RFID tags attached to products transmit data to readers, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and locations.
Comparison of Inventory Tracking Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | – Simple and cost-effective- Suitable for small businesses with low inventory volumes | – Time-consuming- Prone to errors- Limited scalability |
| Automated | – Greater accuracy and efficiency- Real-time inventory visibility- Improved inventory management | – Higher initial investment- Requires specialized equipment- Can be complex to implement |
| RFID | – High accuracy and real-time tracking- Reduced labor costs- Improved inventory visibility | – Expensive to implement- Requires specialized equipment- Can be affected by environmental factors |
Best Practices for Business Inventory Tracking
Establishing effective inventory tracking practices is crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records, minimize losses, and optimize operations. By implementing a comprehensive inventory tracking system, businesses can gain valuable insights into their inventory levels, optimize stock replenishment, and enhance overall efficiency.
Key Considerations for Implementing an Inventory Tracking System
A well-defined checklist of key considerations can guide businesses in implementing a robust inventory tracking system:
- Define clear inventory tracking goals and objectives:Establish specific targets for accuracy, efficiency, and cost reduction.
- Choose the appropriate inventory tracking method:Select the most suitable method based on the business’s size, industry, and inventory turnover rate.
- Implement standardized processes:Establish clear procedures for receiving, storing, and issuing inventory to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Utilize technology:Leverage inventory management software or mobile apps to automate processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance visibility.
- Train staff effectively:Provide comprehensive training to employees responsible for inventory management to ensure proper understanding and execution of best practices.
Importance of Regular Inventory Audits and Cycle Counting
Regular inventory audits and cycle counting are essential for maintaining inventory accuracy and preventing discrepancies.
- Inventory Audits:Periodic physical counts of inventory provide a comprehensive overview of stock levels and identify any variances from the system records. This allows businesses to make necessary adjustments and identify potential theft or shrinkage.
- Cycle Counting:Regularly counting a portion of inventory throughout the year helps businesses identify discrepancies early on and make timely adjustments. This approach is less disruptive than a full inventory audit and provides more frequent visibility into inventory levels.
By implementing best practices for inventory tracking, including establishing clear goals, utilizing technology, and conducting regular audits and cycle counting, businesses can significantly improve inventory management, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Challenges of Business Inventory Tracking
Implementing and maintaining effective inventory tracking systems can pose various challenges for businesses. These challenges may arise from different factors, including system complexities, data accuracy, and operational constraints.
One of the primary challenges lies in ensuring data accuracy. Inventory tracking systems rely on timely and accurate data input to provide meaningful insights. However, manual data entry processes can be prone to errors, leading to incorrect inventory counts and potentially impacting decision-making.
Overcoming Data Accuracy Challenges
- Implement automated data capture systems:Employing barcode scanners, RFID technology, or other automated data capture methods can minimize manual data entry and reduce the risk of errors.
- Establish clear data entry protocols:Define standardized procedures for data entry, including guidelines for data validation and error correction.
- Conduct regular inventory audits:Periodically verify physical inventory counts against system records to identify and rectify any discrepancies.
Another challenge involves managing inventory shrinkage. Inventory shrinkage refers to the loss of inventory due to factors such as theft, damage, or misplacement. This can lead to reduced profitability and operational inefficiencies.
Minimizing Inventory Shrinkage
- Implement robust security measures:Enhance physical security by installing surveillance cameras, access control systems, and limiting access to inventory areas.
- Conduct regular inventory cycle counts:Regularly counting inventory helps identify discrepancies and potential shrinkage issues.
- Train staff on inventory handling procedures:Educate employees on proper inventory handling techniques to minimize damage and loss.
Overall, addressing these challenges requires a combination of technological solutions, process improvements, and employee training. By implementing effective measures, businesses can enhance the accuracy and reliability of their inventory tracking systems, minimize inventory shrinkage, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Business Inventory Tracking
The landscape of business inventory tracking is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-changing needs of businesses. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain are poised to revolutionize the way businesses manage their inventory, leading to increased efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings.
AI and ML in Inventory Management
AI and ML algorithms can be used to analyze vast amounts of data related to inventory levels, sales patterns, and supply chain dynamics. This data can be leveraged to predict future demand, optimize inventory levels, and identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
By automating these tasks, businesses can free up their resources and focus on more strategic initiatives.
Blockchain for Secure and Transparent Inventory Tracking
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to track inventory throughout the supply chain. By creating a distributed ledger that records all transactions, businesses can gain real-time visibility into the movement of goods, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring the integrity of inventory data.
The Future of Inventory Tracking
The convergence of these emerging technologies will shape the future of inventory tracking, enabling businesses to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and optimization. Real-time inventory visibility, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making will become the norm, leading to improved customer service, reduced costs, and increased profitability.
Outcome Summary
The content of the concluding paragraph that provides a summary and last thoughts in an engaging manner
Question & Answer Hub
What is business inventory tracking?
Business inventory tracking is the process of monitoring and managing the flow of goods within a business, from the point of purchase to the point of sale.
What are the benefits of business inventory tracking?
The benefits of business inventory tracking include improved accuracy, reduced costs, increased efficiency, and better customer service.
What are the challenges of business inventory tracking?
The challenges of business inventory tracking include managing inventory levels, preventing shrinkage, and keeping track of inventory in multiple locations.
